178x Filetype PDF File size 1.11 MB Source: www.madison-lake.k12.oh.us
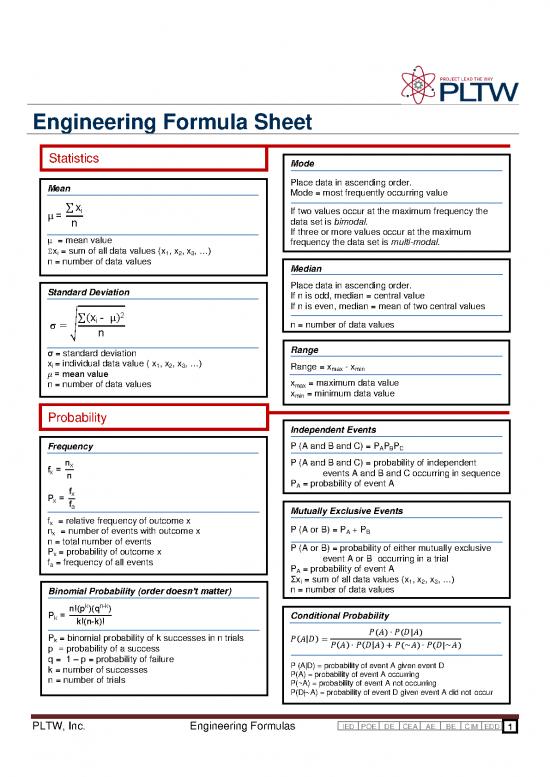
Engineering Formula Sheet
Statistics
Mode
Mean Place data in ascending order.
Mode = most frequently occurring value
∑x
If two values occur at the maximum frequency the
data set is bimodal.
If three or more values occur at the maximum
µ = mean value frequency the data set is multi-modal.
Σx = sum of all data values (x , x , x , …
i 1 2 3
n = number of data values Median
Standard Deviation Place data in ascending order.
If n is odd, median = central value
If n is even, median = mean of two central values
∑(x )
√ n = number of data values
Range
σ = standard deviation
x = individual data value ( x , x , x , …
i 1 2 3 Range = x - x
max min
n = number of data values x = maximum data value
max
x = minimum data value
min
Probability
Independent Events
Frequency P (A and B and C) = P P P
A B C
P (A and B and C) = probability of independent
x
x events A and B and C occurring in sequence
P = probability of event A
A
x
x
Mutually Exclusive Events
f = relative frequency of outcome x
x P (A or B) = P + P
n = number of events with outcome x A B
x
n = total number of events P (A or B) = probability of either mutually exclusive
P = probability of outcome x
x event A or B occurring in a trial
f = frequency of all events
a P = probability of event A
A
Σx = sum of all data values (x , x , x , …
i 1 2 3
n = number of data values
Binomial Probability (order doesn’t matter)
Conditional Probability
P = binomial probability of k successes in n trials ( ) ( | )
( | )
k
( ) ( | )
p = probability of a success ( ) ( | )
q = 1 – p = probability of failure
k = number of successes P (A|D) = probability of event A given event D
n = number of trials P(A) = probability of event A occurring
P(~A) = probability of event A not occurring
P(D| ~A) = probability of event D given event A did not occur
PLTW, Inc. Engineering Formulas IED POE DE CEA AE BE CIM EDD 1
Plane Geometry Ellipse Rectangle
2b
Circle Perimeter = 2a + 2b
2a Area = ab
Triangle B
Parallelogram c
Area = ½ bh a h
h 2 2 2
Area = bh a = b + c – 2bc·cos∠A A
2 2 2 C
b = a + c – 2ac·cos∠B b
b 2 2 2
c = a + b – 2ab·cos∠C
Right Triangle Regular Polygons s
f
2 2 2
c = a + b
a c
n = number of sides
θ
b Trapezoid a
h
Area = ½(a + b)h h
h
Solid Geometry b
h
Cube Sphere
3 s
Volume = s r
2 3
Surface Area = 6s Volume r
s s 2
Surface Area = 4 r
Rectangular Prism Cylinder
r
h
Volume = wdh 2 h
Surface Area = 2(wd + wh + dh) w d Volume = r h 2
Surface Area = 2 rh+2 r
Right Circular Cone
h
Irregular Prism
r h
√ Volume = Ah
A = area of base
Pyramid
h Constants
2 2
A = area of base g = 9.8 m/s = 32.27 ft/s
-11 3 2
G = 6.67 x 10 m/kg·s
π = 3.14159
PLTW, Inc. Engineering Formulas IED POE DE CEA AE BE CIM EDD 2
Conversions
Mass Area Force Energy
2
1 kg = 2.205 lbm 1 acre = 4047 m 1 N = 0.225 lbf 1 J = 0.239 cal
2 -4
1 slug = 32.2 lbm = 43,560 ft 1 kip = 1,000 lbf = 9.48 x 10 Btu
2
1 ton = 2000 lbm = 0.00156 mi = 0.7376 ft·lbf
Pressure 1kW h = 3,6000,000 J
Length Volume 1 atm = 1.01325 bar
= 33.9 ft H O
1 m = 3.28 ft 1L = 0.264 gal 2 Defined Units
3 = 29.92 in. Hg
1 km = 0.621 mi = 0.0353 ft = 760 mm Hg
1 in. = 2.54 cm = 33.8 fl oz = 101,325 Pa
3 1 J = 1 N·m
1 mi = 5280 ft 1mL = 1 cm = 1 cc = 14.7 psi 2
1 yd = 3 ft 1 N = 1 kg·m / s
1psi = 2.31 ft of H O 2
Time 2 1 Pa = 1 N / m
1 V = 1 W / A
Temperature Change 1 d = 24 h Power 1 W = 1 J / s
1 h = 60 min 1 W = 1 V / A
1 K = 1 ºC 1 W = 3.412 Btu/h -1
= 1.8 ºF 1 min = 60 s = 0.00134 hp 1 Hz = 1 s
= 1.8 ºR 1 yr = 365 d = 14.34 cal/min 1 F = 1 A·s / V
= 0.7376 ft·lb/s 1 H = 1 V·s / V
f
SI Prefixes
Numbers Less Than One Numbers Greater Than One
Power of 10 Prefix Abbreviation Power of 10 Prefix Abbreviation
-1 1
10 deci- d 10 deca- da
-2 2
10 centi- c 10 hecto- h
-3 3
10 milli- m 10 kilo- k
-6 6
10 micro- µ 10 Mega- M
-9 9
10 nano- n 10 Giga- G
10-12 pico- p 1012 Tera- T
10-15 femto- f 1015 Peta- P
10-18 atto- a 1018 Exa- E
10-21 zepto- z 1021 Zetta- Z
10-24 yocto- y 1024 Yotta- Y
Equations Temperature Force
T = T + 273 F = ma
Mass and Weight K C
F = force
TR = TF + 460 m = mass
M = VDm a = acceleration
W = mg
W = VD Equations of Static Equilibrium
w
V = volume
ΣF = 0 ΣF = 0 ΣM = 0
T = temperature in Kelvin x y P
D = mass density K
m TC = temperature in Celsius F = force in the x-direction
m = mass T = temperature in Rankin x
D = weight density R Fy = force in the y-direction
w TF = temperature in Fahrenheit M = moment about point P
g = acceleration due to gravity P
PLTW, Inc. Engineering Formulas IED POE DE CEA AE BE CIM EDD 3
Equations (Continued)
Electricity
Ohm’s Law
Energy: Work Fluid Mechanics V = IR
P = IV
W = work
R (series) = R + R + ··· + R
T 1 2 n
F = force ’ L
d = distance
(Guy-L ’ L
Power
Kirchhoff’s Current Law
P V = P V B y ’ L
1 1 2 2 I = I + I + ··· + I
T 1 2 n
∑
or
Q = Av
A v = A v Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law
1 1 2 2
V = V + V + ··· + V
T 1 2 n
∑
P = power or
E = energy
W = work absolute pressure = gauge pressure V = voltage
t = time + atmospheric pressure V = total voltage
τ = torque T
rpm = revolutions per minute P = absolute pressure I = current
I = total current
F = Force T
A = Area R = resistance
Efficiency V = volume RT = total resistance
T = absolute temperature P = power
Q = flow rate
y v = flow velocity
Thermodynamics
P = useful power output ′ ∆T
out Mechanics
P = total power input
in
(where acceleration = 0)
∆
Energy: Potential
(where acceleration = 0)
L
U = potential energy
m =mass L
g = acceleration due to gravity A v = A v
h = height 1 1 2 2
v = v + at
0
Energy: Kinetic d = d + v t + ½at2 P = rate of heat transfer
0 0 Q = thermal energy
2 2
v = v + 2a(d – d )
0 0
A = Area of thermal conductivity
K = kinetic energy τ = dFsinθ U = coefficient of heat conductivity
m = mass (U-factor)
v = velocity s = speed ∆T = change in temperature
v = velocity
a = acceleration R = resistance to heat flow ( R-value)
Energy: Thermal X = range k = thermal conductivity
t = time v = velocity
d = distance P = net power radiated
net
g = acceleration due to gravity -8
= 5.6696 x 10
Q = thermal energy d = distance
m = mass θ = angle e = emissivity constant
c = specific heat T , T = temperature at time 1, time 2
∆T = change in temperature τ = torque 1 2
F = force
PLTW, Inc. Engineering Formulas v = flow velocity POE 4 DE 4
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.